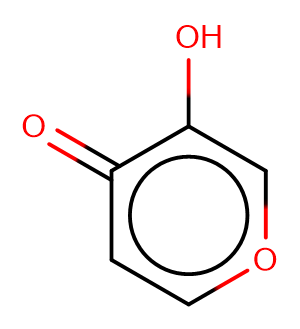
Pyromeconic acid
CAS No. 496-63-9
Pyromeconic acid( 3-hydroxy-4H-pyran-4-one )
Catalog No. M21209 CAS No. 496-63-9
Pyromeconic acid and derivatives thereof are potent inhibitors of endonuclease.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 10MG | 45 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 74 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 106 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 157 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NamePyromeconic acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionPyromeconic acid and derivatives thereof are potent inhibitors of endonuclease.
-
DescriptionPyromeconic acid and derivatives thereof are potent inhibitors of endonuclease.
-
In VitroThe minimum concentration of Pyromeconic acid to show inhibition of fungal growth on silica gel-coated glass plates is 15 μg/80 mm2.Pyromeconic acid has water-soluble and siderophilic nature.
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms3-hydroxy-4H-pyran-4-one
-
PathwayMicrobiology/Virology
-
TargetAntifection
-
RecptorAntifection
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number496-63-9
-
Formula Weight112.08
-
Molecular FormulaC5H4O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESOc1coccc1=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Hashidoko Yasuyuki. Pyromeconic Acid and Its Glucosidic Derivatives from Leaves of\r Erigeron annuus\r and the Siderophile Activity of Pyromeconic Acid[J]. Bioscience Biotechnology & Biochemistry 1995 59(5):886-890.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Chlorhexidine hydroc...
Chlorhexidine dihydrochloride is an antibacterial, used as an antiseptic and for other applications.
-
57-DIMETHOXYFLAVONE
57-DIMETHOXYFLAVONE possessed remarkable leishmanicidal potential.
-
2-Desoxy-4-epi-pulch...
2-Desoxy-4-epi-pulchellin has potent in vitro cytotoxicities against the K562, MCF-7, Hela, DU145, U937, H1975, SGC-7901, A549, MOLT-4, and HL60 cell lines with IC50 values ranging from 0.10 to 46.7uM.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


